Cannabis contains over 483 active compounds, 80 of which are cannabinoids. This means that there are far more different variables that affect the body than just THC or CBD. Therefore new scientific research is and will be necessary in order to improve our understanding of very controversial plant.
The 80 compounds only found in cannabis are known as cannabinoids. These interact with the receptors in our body to induce effects within our nervous system and brain. Coincidence or not, humans have a system that can interact with cannabinoids, called endocannabinoids system.
We will briefly outline below the 8 major cannabinoids found within marijuana.
THC
 This is the most commonly recognized and abundantly found cannabinoid within cannabis; it stands for delta-9-tetrahydrocannibinol. This cannabinoid is responsible to the main psychoactive effect experienced when consuming cannabis, it stimulates parts of the brain causing the release of dopamine – creating a sense of euphoria and well being. THC also has analgesic effects, relieving the symptoms of pain and inflammation. Combined they cause a great sense of relaxation.
This is the most commonly recognized and abundantly found cannabinoid within cannabis; it stands for delta-9-tetrahydrocannibinol. This cannabinoid is responsible to the main psychoactive effect experienced when consuming cannabis, it stimulates parts of the brain causing the release of dopamine – creating a sense of euphoria and well being. THC also has analgesic effects, relieving the symptoms of pain and inflammation. Combined they cause a great sense of relaxation.
CBD
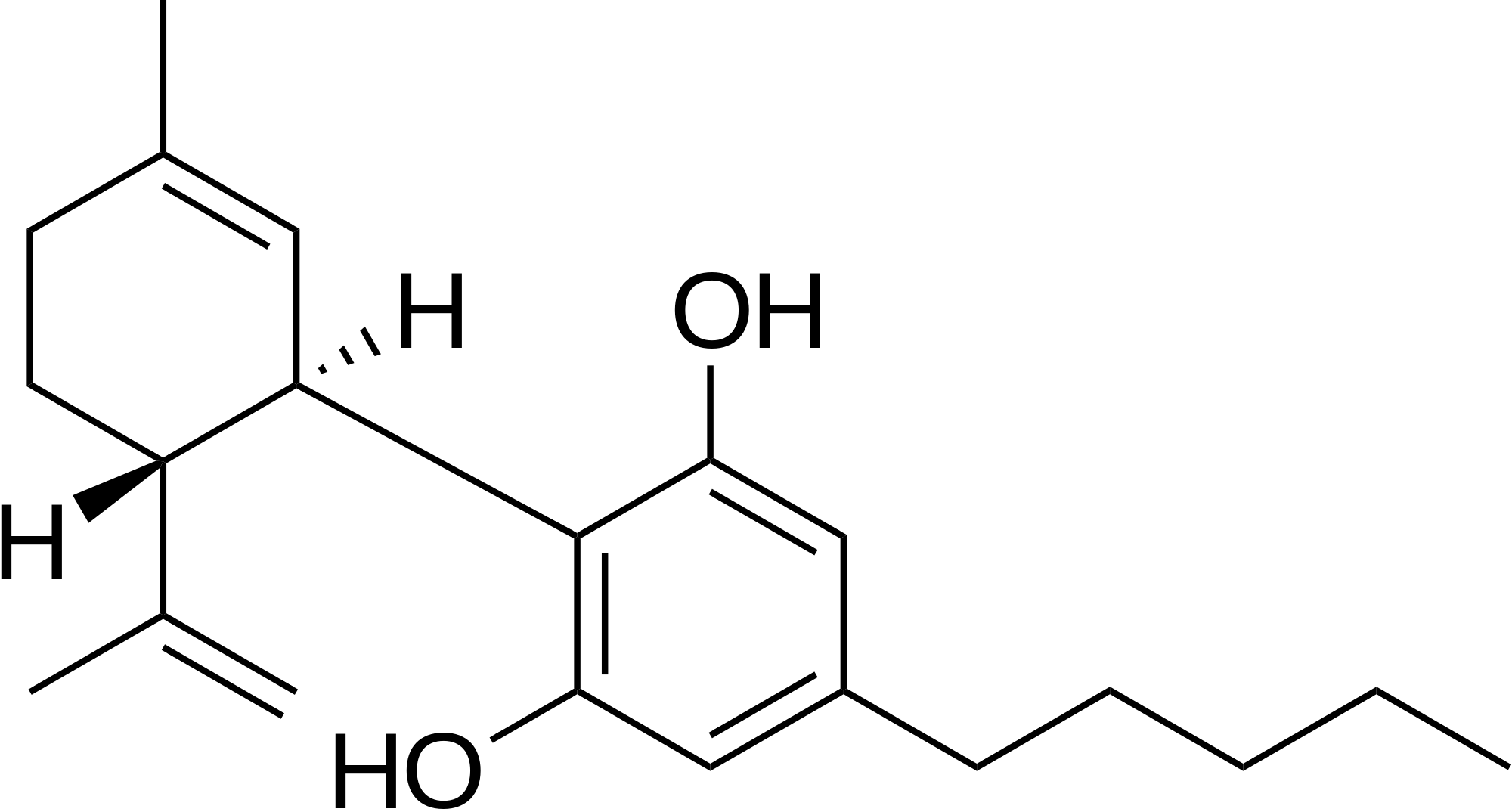 Cannabidiol, or CBD for short, tends to be the second most abundant cannabinoid in marijuana. It has serious implications into the field of medicine, and is the sought after compound by medical users. It is a non-psychoactive component that is believed to reduce and regulate the effects of THC. This means that strains high in THC and CBD will induce much clearer head highs than more hazy, heady strains containing very little CBD. CBD itself has a long list of medicinal properties. The main of which relieve things such as chronic pain, inflammation, migraines, arthritis, spasms and epilepsy and schizophrenia. CBD has also been show to have some anti cancer properties, and new uses are being found all the time as more research is conducted.
Cannabidiol, or CBD for short, tends to be the second most abundant cannabinoid in marijuana. It has serious implications into the field of medicine, and is the sought after compound by medical users. It is a non-psychoactive component that is believed to reduce and regulate the effects of THC. This means that strains high in THC and CBD will induce much clearer head highs than more hazy, heady strains containing very little CBD. CBD itself has a long list of medicinal properties. The main of which relieve things such as chronic pain, inflammation, migraines, arthritis, spasms and epilepsy and schizophrenia. CBD has also been show to have some anti cancer properties, and new uses are being found all the time as more research is conducted.
CBN
 Cannabinol, or CBN for short, is an analgesic that is created from the break down of THC through oxidization. It is mildly psychoactive and is only found in small quantities within fresh cannabis plants. It can be kept to a minimum by keeping harvested cannabis stored in a dark, dry place. The effects of THC tend to be preferred to CBN – as CBN is not as strong as THC and can cause grogginess when found in high concentrates. It is also known to reduce anxiety and relieve pressure behind the eyes.
Cannabinol, or CBN for short, is an analgesic that is created from the break down of THC through oxidization. It is mildly psychoactive and is only found in small quantities within fresh cannabis plants. It can be kept to a minimum by keeping harvested cannabis stored in a dark, dry place. The effects of THC tend to be preferred to CBN – as CBN is not as strong as THC and can cause grogginess when found in high concentrates. It is also known to reduce anxiety and relieve pressure behind the eyes.
CBG
 CBG, also known as cannabigerol, is an active compound in cannabis that is mostly known for its anti-bacterial effects. However, very recent research has found that, whilst not traditionally though to be very prevalent within most cannabis strains, it is likely to be the “template” or “stem cell” for both THC and CBD. This means that both THC and CBD start out as CBG. CBG has also been found to inhibit the uptake of GABA, this causes a feeling of relaxation that is normally associated with CBD. These findings have spurred new ongoing research into the cannabinoid, meaning it may have even larger implications.
CBG, also known as cannabigerol, is an active compound in cannabis that is mostly known for its anti-bacterial effects. However, very recent research has found that, whilst not traditionally though to be very prevalent within most cannabis strains, it is likely to be the “template” or “stem cell” for both THC and CBD. This means that both THC and CBD start out as CBG. CBG has also been found to inhibit the uptake of GABA, this causes a feeling of relaxation that is normally associated with CBD. These findings have spurred new ongoing research into the cannabinoid, meaning it may have even larger implications.
Possible advantages of CBG?
THCV
 Tetrahydrocannabivarin, or THCV for short, is thought to be a cannabinoid that moderates the intensity of the psychoactive effects of THC. Current research being conducted into THCV also suggests that it can be used to treat metabolic disorders and act as an appetite suppressant.
Tetrahydrocannabivarin, or THCV for short, is thought to be a cannabinoid that moderates the intensity of the psychoactive effects of THC. Current research being conducted into THCV also suggests that it can be used to treat metabolic disorders and act as an appetite suppressant.
CBC
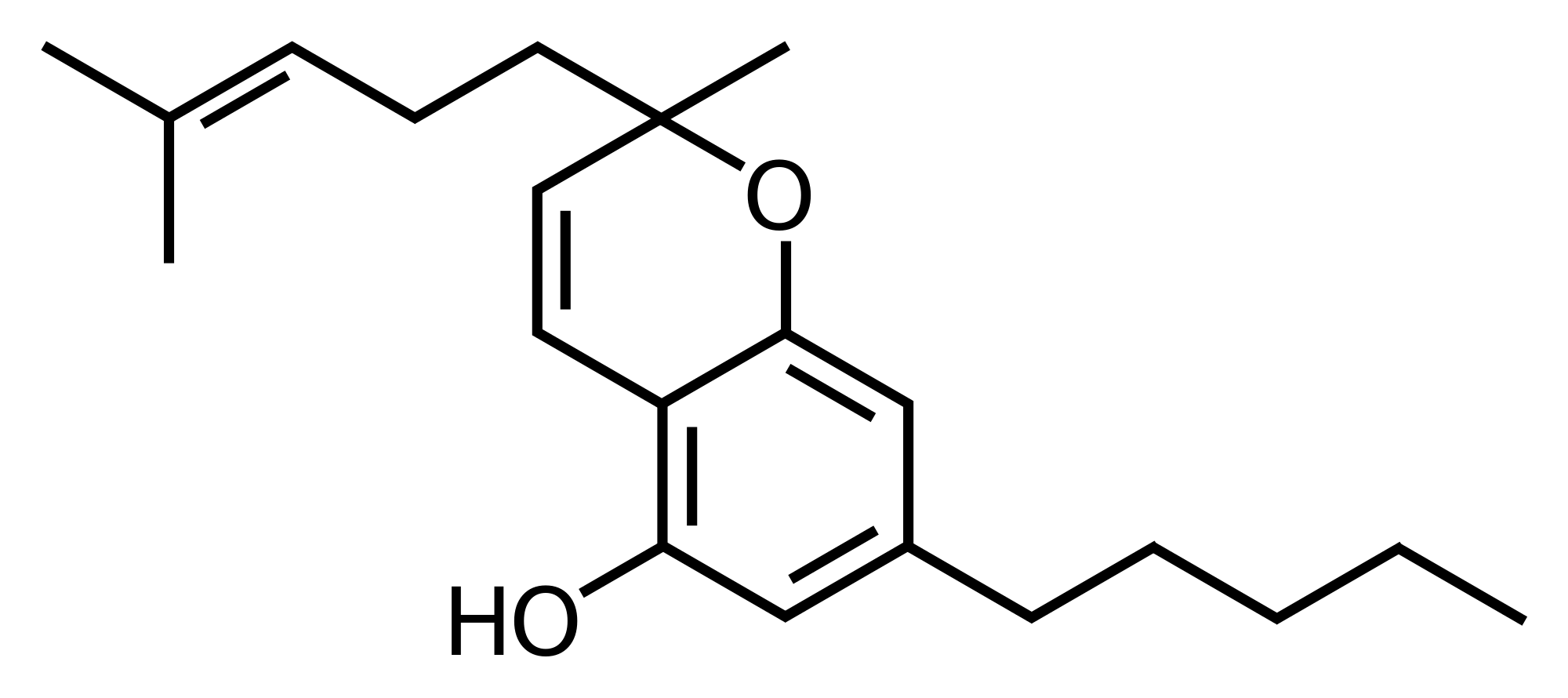 Cannabichromene, or CBC for short, is thought to have anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects, although not much medical research has been conducted into the cannabinoid. Recent research that has been done suggests that it could have a potential role to play in brain cell regrowth.
Cannabichromene, or CBC for short, is thought to have anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects, although not much medical research has been conducted into the cannabinoid. Recent research that has been done suggests that it could have a potential role to play in brain cell regrowth.
THCA
 THCA is the acid form of THC. It is a raw state in which THC can be found in fresh cannabis plants. It is when cannabis is heated that THCA converts to THC. When it is in this raw form, THCA is not considered to be an active compound.
THCA is the acid form of THC. It is a raw state in which THC can be found in fresh cannabis plants. It is when cannabis is heated that THCA converts to THC. When it is in this raw form, THCA is not considered to be an active compound.
CBDA
 Much like THCA, CBDA is the acid form of CBD. It is currently thought to have antimetic (anti-nausea) effects as well as helping to fight breast cancer. However, more research into its medical benefits is needed.
Much like THCA, CBDA is the acid form of CBD. It is currently thought to have antimetic (anti-nausea) effects as well as helping to fight breast cancer. However, more research into its medical benefits is needed.
 Based on +200
reviews
Based on +200
reviews

